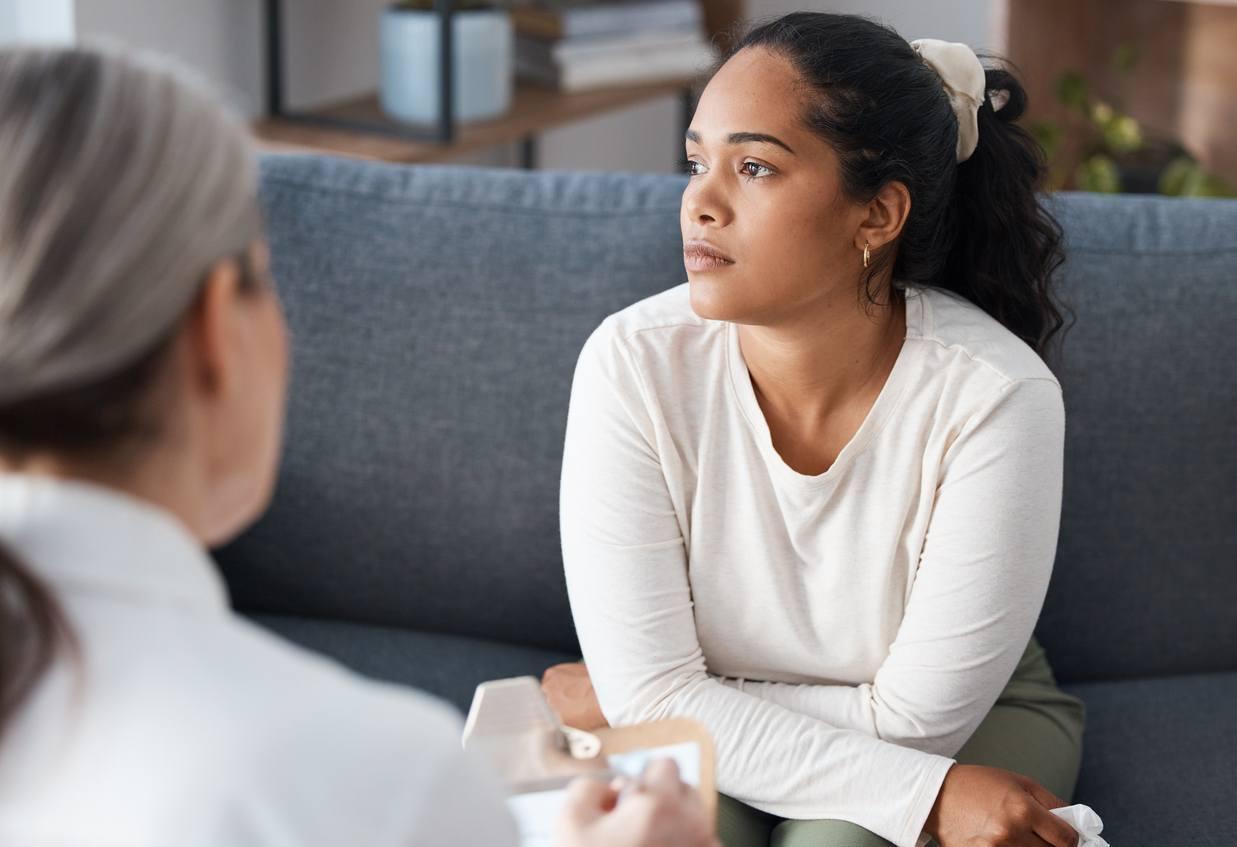
Bipolar disorder, also known as manic-depressive illness, is a complex and chronic mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings that include emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression). These mood swings can affect sleep, energy, behavior, judgment, and the ability to think clearly. The exact cause of bipolar disorder is unknown, but a combination of genetics, environment, and altered brain structure and chemistry may play a role.
Symptoms and Types of Bipolar Disorder
There are several types of bipolar disorder, each defined by the pattern and intensity of the mood episodes:
Bipolar I Disorder: Characterized by manic episodes lasting at least seven days or by manic symptoms that are so severe that immediate hospital care is needed. Depressive episodes occur as well, typically lasting at least two weeks.
Bipolar II Disorder: Defined by a pattern of depressive episodes and hypomanic episodes, which are less severe than the manic episodes seen in Bipolar I Disorder.
Cyclothymic Disorder: Periods of hypomanic symptoms and periods of depressive symptoms lasting for at least two years (one year in children and adolescents) without fulfilling the diagnostic criteria for hypomanic and depressive episodes.
Other Specified and Unspecified Bipolar and Related Disorders: Bipolar disorder symptoms that do not match the three categories listed above.
The Role of Therapy in Managing Bipolar Disorder
Therapy is a crucial component of the treatment plan for bipolar disorder, often used in conjunction with medication to manage symptoms and improve overall functioning. Various therapeutic approaches can be employed based on individual needs and preferences.
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a widely used and effective therapeutic approach for bipolar disorder. It focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to mood swings. CBT helps individuals with bipolar disorder to:
- Recognize early signs of mood changes and triggers
- Develop coping strategies for managing stress and emotional dysregulation
- Challenge and reframe irrational or harmful thoughts
- Establish a stable routine for sleep, exercise, and daily activities
2. Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT)
IPSRT is designed specifically for individuals with bipolar disorder. This therapy emphasizes the importance of maintaining regular daily routines and stable interpersonal relationships to prevent mood episodes. IPSRT involves:
- Tracking daily routines and identifying patterns that may disrupt mood stability
- Developing strategies to maintain consistent sleep and activity schedules
- Addressing and improving interpersonal relationships and communication skills
- Managing life changes and stressors that can trigger mood episodes
3. Psychoeducation
Psychoeducation involves educating individuals with bipolar disorder and their families about the condition, its symptoms, and treatment options. This approach aims to:
- Enhance understanding of the disorder and its impact on daily life
- Foster collaboration between the individual, family, and healthcare providers
- Empower individuals to recognize early signs of mood episodes and seek timely intervention
- Reduce stigma and promote acceptance of the condition
4. Family-Focused Therapy (FFT)
FFT involves the individual’s family in the treatment process to improve communication, problem-solving skills, and support within the family unit. FFT focuses on:
- Educating family members about bipolar disorder
- Enhancing family communication and reducing conflict
- Developing strategies for managing stress and crises
- Encouraging a supportive and understanding home environment
5. Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
Originally developed for borderline personality disorder, DBT has been adapted for bipolar disorder due to its focus on emotion regulation and distress tolerance. DBT helps individuals to:
- Develop mindfulness skills to stay present and focused
- Improve emotional regulation to manage intense mood swings
- Enhance interpersonal effectiveness to navigate relationships more effectively
- Build distress tolerance skills to cope with crisis situations without resorting to harmful behaviors
6. Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT)
MBCT combines elements of CBT with mindfulness practices. This approach helps individuals with bipolar disorder to:
- Develop a greater awareness of their thoughts and feelings
- Cultivate a non-judgmental attitude towards their experiences
- Reduce rumination and prevent depressive relapses
- Enhance overall emotional well-being
Integrating Therapy with Medication
While therapy is a vital component of treatment for bipolar disorder, medication management is often necessary to stabilize mood and prevent recurrent episodes. Common medications used include mood stabilizers (such as lithium), antipsychotic medications, and antidepressants. The combination of medication and therapy can:
- Provide more comprehensive symptom management
- Address both the biological and psychological aspects of the disorder
- Enhance adherence to treatment and improve long-term outcomes
Conclusion
Bipolar disorder is a lifelong condition that requires ongoing management and support. Therapeutic approaches, when integrated with medication and a strong support system, can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with bipolar disorder. By addressing the psychological, behavioral, and social aspects of the condition, therapy helps individuals develop the skills and resilience needed to navigate the challenges of bipolar disorder and lead fulfilling lives.