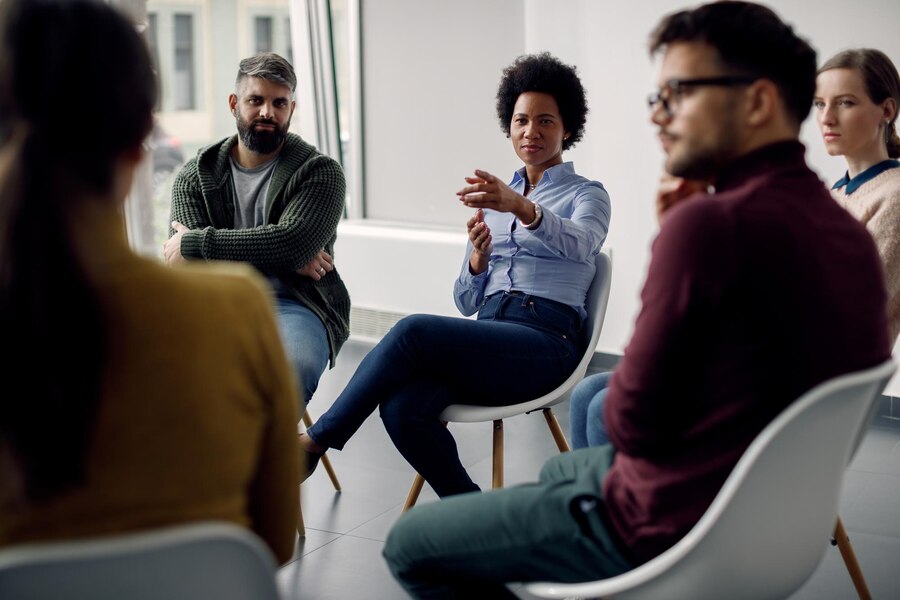
Mental and emotional illnesses can have profound effects on an individual’s social health, influencing their ability to form and maintain relationships, engage in social activities, and function effectively in various social settings. This article explores the intricate connection between mental health and social well-being, shedding light on the challenges faced by those with mental and emotional illnesses and the broader implications for society.
Understanding Mental and Emotional Illnesses
Mental and emotional illnesses encompass a wide range of conditions that affect mood, thinking, and behavior. These can include:
- Depression
- Anxiety disorders
- Bipolar disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Eating disorders
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
Each of these conditions can manifest differently, but they all have the potential to impact an individual’s social functioning and overall quality of life.
The Social Health Dimension
Social health refers to an individual’s ability to form meaningful relationships, interact effectively with others, and participate in social activities. It is a crucial component of overall well-being, alongside physical and mental health. Good social health contributes to:
- Emotional support
- Sense of belonging
- Personal growth
- Stress reduction
- Improved self-esteem
When mental and emotional illnesses interfere with social health, the consequences can be far-reaching and long-lasting.
How Mental and Emotional Illnesses Affect Social Health
1. Relationship Challenges
Mental and emotional illnesses can strain existing relationships and make it difficult to form new ones. Individuals may experience:
- Difficulty expressing emotions
- Withdrawal from social interactions
- Misinterpretation of social cues
- Increased conflict due to mood swings or irritability
- Fear of rejection or judgment
These challenges can lead to isolation and loneliness, further exacerbating mental health issues.
2. Social Stigma and Discrimination
Despite increased awareness, mental health stigma persists in many societies. This can result in:
- Social exclusion
- Workplace discrimination
- Reduced opportunities for education and employment
- Reluctance to seek help or treatment
The fear of stigma can cause individuals to hide their conditions, leading to delayed treatment and worsened outcomes.
3. Impaired Social Skills
Some mental illnesses can affect cognitive functions and social skills, making it challenging to:
- Maintain conversations
- Understand non-verbal cues
- Empathize with others
- Manage conflicts effectively
These impairments can lead to misunderstandings and social difficulties in various settings.
4. Reduced Social Participation
Mental and emotional illnesses often result in decreased participation in social activities:
- Avoidance of social gatherings
- Reduced involvement in community events
- Withdrawal from hobbies and interests
- Limited social network
This reduction in social engagement can further impact mental health, creating a cycle of isolation and worsening symptoms.
5. Family Dynamics
Mental illness doesn’t just affect the individual; it can also strain family relationships:
- Increased caregiver burden
- Communication difficulties
- Role changes within the family
- Financial stress due to treatment costs or lost income
These factors can lead to family conflicts and disrupted home environments.
The Ripple Effect on Society
The impact of mental and emotional illnesses on social health extends beyond the individual, affecting society as a whole:
- Economic Impact: Reduced productivity, increased healthcare costs, and disability benefits contribute to significant economic burden.
- Public Health: Untreated mental illnesses can lead to other health problems, substance abuse, and in severe cases, homelessness or incarceration.
- Social Cohesion: Widespread mental health issues can erode community bonds and social trust.
- Generational Effects: Children of parents with mental illnesses may face increased risks of developing mental health problems themselves.
Read More: What is Difference Between Interpersonal and Intrapersonal Communication
Strategies for Improving Social Health
While mental and emotional illnesses pose significant challenges to social health, there are strategies to mitigate their impact:
- Early Intervention: Recognizing and treating mental health issues early can prevent long-term social consequences.
- Comprehensive Treatment: Addressing both mental health symptoms and social skills through therapy, medication, and social skills training.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide validation and practical coping strategies.
- Public Education: Increasing awareness and understanding of mental health can reduce stigma and promote inclusion.
- Workplace Accommodations: Implementing policies that support employees with mental health conditions can improve job retention and productivity.
- Community Programs: Developing initiatives that foster social connections and support for individuals with mental illnesses.
Table: Common Mental Illnesses and Their Social Impact
| Mental Illness | Primary Symptoms | Social Health Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Depression | Persistent sadness, loss of interest | Social withdrawal, reduced participation in activities |
| Anxiety Disorders | Excessive worry, fear | Avoidance of social situations, difficulty forming relationships |
| Bipolar Disorder | Mood swings (mania and depression) | Strained relationships due to unpredictable behavior |
| Schizophrenia | Delusions, hallucinations | Social isolation, difficulty maintaining employment |
| PTSD | Flashbacks, hypervigilance | Trust issues, challenges in intimate relationships |
| OCD | Intrusive thoughts, compulsive behaviors | Social awkwardness, limited social activities due to rituals |
FAQs
Q1: Can mental illness cause permanent damage to social relationships?
A1: While mental illness can strain relationships, with proper treatment and support, many individuals can repair and strengthen their social connections. However, some relationships may change or end due to the challenges posed by mental health issues.
Q2: How can I support a friend or family member with a mental illness?
A2: Offer empathy and understanding, educate yourself about their condition, encourage professional help, and maintain open communication. Be patient and avoid judgment or criticism.
Q3: Are there any positive aspects to mental illness in terms of social health?
A3: While mental illness primarily poses challenges, some individuals report increased empathy, creativity, and deeper connections with others who have similar experiences. These qualities can contribute positively to social interactions when symptoms are well-managed.
Q5: Can improving social health help alleviate symptoms of mental illness?
A5: Yes, strengthening social connections and improving social skills can have a positive impact on mental health. Social support acts as a buffer against stress and can improve overall well-being, potentially reducing the severity of mental health symptoms.
Conclusion
The relationship between mental and emotional illnesses and social health is complex and multifaceted. While these conditions can significantly impact an individual’s ability to form and maintain social connections, understanding these challenges is the first step toward developing effective interventions and support systems. By addressing both the mental health symptoms and social aspects of well-being, we can work towards a more inclusive society that promotes the overall health and happiness of all individuals, regardless of their mental health status.