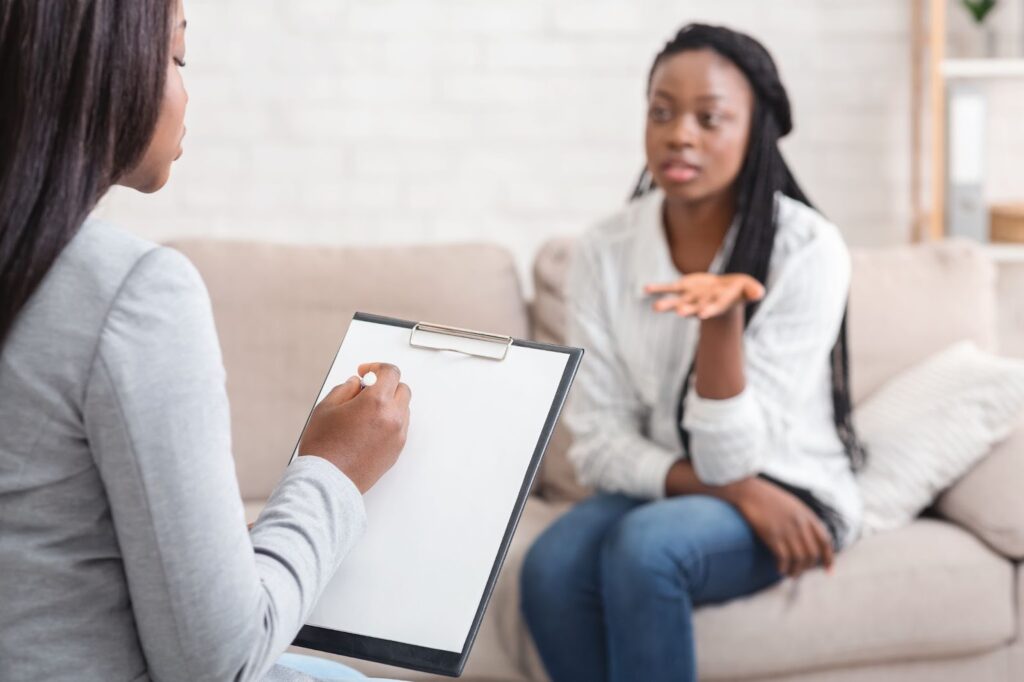
Psychotherapy, often referred to as talk therapy or counseling, is a collaborative treatment approach that aims to help individuals with a variety of mental health issues, emotional challenges, and behavioral difficulties. It involves conversations between a trained therapist and a client, with the goal of exploring feelings, thoughts, behaviors, and experiences in a safe and supportive environment. Psychotherapy can be beneficial for people of all ages, backgrounds, and walks of life, and it is often used to address issues such as depression, anxiety, trauma, relationship problems, grief, and stress.
Key Components of Psychotherapy:
Therapeutic Relationship: Central to psychotherapy is the therapeutic relationship between the therapist and the client. This relationship is built on trust, empathy, and understanding, and it provides a supportive space for clients to explore their thoughts and feelings without fear of judgment.
Exploration and Insight: Psychotherapy involves exploring the client’s thoughts, emotions, behaviors, and past experiences to gain insight into their patterns and challenges. Through this process, clients can develop a deeper understanding of themselves and their motivations, which can lead to positive changes in their lives.
Goal Setting: Therapy sessions often involve setting goals and objectives for the client to work towards. These goals may be related to improving mood, changing behaviors, developing coping skills, or resolving conflicts. By working towards specific goals, clients can track their progress and stay motivated throughout the therapeutic process.
Evidence-Based Techniques: Therapists use a variety of evidence-based techniques and approaches to help clients achieve their goals. These may include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), psychodynamic therapy, mindfulness-based therapies, and more. The specific approach used will depend on the client’s needs, preferences, and the therapist’s expertise.
Cultural Sensitivity: It’s important for therapists to be culturally sensitive and aware of the diverse backgrounds and experiences of their clients. Cultural factors such as language, religion, values, and traditions can influence a person’s mental health and wellbeing, so therapists strive to create a culturally responsive and inclusive therapeutic environment.
Types of Psychotherapy:
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and beliefs that contribute to emotional distress and problematic behaviors. It teaches clients to develop more adaptive ways of thinking and coping with stressors.
Psychodynamic Therapy: Individual Therapy explores how past experiences, particularly those from childhood, influence current thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It aims to uncover unconscious conflicts and patterns in order to promote insight and healing.
Humanistic Therapy: Humanistic therapy emphasizes personal growth, self-actualization, and the inherent worth of each individual. Therapists provide empathy, unconditional positive regard, and genuineness to help clients explore their feelings and values.
Mindfulness-Based Therapies: These therapies, such as mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), incorporate mindfulness practices to help clients develop present-moment awareness, acceptance, and non-judgmental attitudes towards their experiences.
Family Therapy: Family therapy involves working with families and couples to improve communication, resolve conflicts, and strengthen relationships. It recognizes the interconnectedness of family dynamics and how they influence individual members’ mental health.
Benefits of Psychotherapy:
Improved Emotional Wellbeing: Psychotherapy provides a safe and supportive space for individuals to express their thoughts and feelings, leading to reduced emotional distress and an increased sense of wellbeing.
Enhanced Coping Skills: Therapy equips clients with effective coping skills and strategies to manage stress, regulate emotions, and navigate life’s challenges more effectively.
Greater Self-Awareness: Through the therapeutic process, clients gain insight into their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, leading to a deeper understanding of themselves and their relationships.
Better Relationships: Therapy can improve communication skills, empathy, and conflict resolution abilities, leading to healthier and more satisfying relationships with others.
Symptom Reduction: Psychotherapy has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms of various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, PTSD, and eating disorders.
Increased Resilience: By developing coping skills, problem-solving abilities, and a supportive network, individuals become more resilient in the face of adversity and life’s challenges.
Conclusion:
Psychotherapy is a valuable and effective treatment approach for addressing a wide range of mental health issues and emotional difficulties. Through the therapeutic process, individuals can gain insight, develop coping skills, and experience positive changes in their lives. Whether you’re struggling with depression, anxiety, relationship problems, or simply seeking personal growth and self-discovery, psychotherapy can provide the support and guidance you need to thrive. Remember, it’s okay to seek help, and taking that step towards therapy can be the first step towards healing and transformation.